

Next: Multi-Subject FMRI data
Up: Multi-Session FMRI data
Previous: Multi-Session FMRI data
The data were individually corrected for head-motion using
MCFLIRT. Mean-based intensity normalisation of all volumes by
the same factor was applied (i.e. grand-mean scaling so that each of the 10
sessions had the same mean intensity value when averaged over 78
volumes and all brain voxels), followed by high-pass temporal filtering (see
above) was performed. The individual data sets were registered into
the space of the high resolution T1 image using
FLIRT [Jenkinson and Smith, 2001]. In order to decrease computational load,
the T1 high resolution image was segmented into different tissue types
using FMRIB's Automated Segmentation Tool (FAST) [Zhang et al., 2001]. This
provided maximum a-posteriori estimates for voxel-wise grey matter
probability. Voxels with 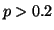 (N=47168;
(N=47168; 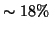 of all intra-cranial voxels) were included in the tensor
analysis so that
of all intra-cranial voxels) were included in the tensor
analysis so that
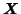 is a 3-way array of dimension
is a 3-way array of dimension
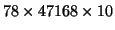 . Based on the estimated sample covariance matrix of
the
. Based on the estimated sample covariance matrix of
the
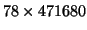 matrix
matrix
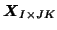 , the Laplace
approximation to the model estimated a 19-dimensional signal sub-space. The data for each session was projected onto the space spanned by the first 19
Eigenvectors and spatially normalised by the voxel-wise variance
estimate from the residuals of the projection.
, the Laplace
approximation to the model estimated a 19-dimensional signal sub-space. The data for each session was projected onto the space spanned by the first 19
Eigenvectors and spatially normalised by the voxel-wise variance
estimate from the residuals of the projection.


Next: Multi-Subject FMRI data
Up: Multi-Session FMRI data
Previous: Multi-Session FMRI data
Christian Beckmann
2004-12-14