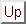

Next: Conclusion
Up: Examples
Previous: Numerical simulation
 -tests
-tests
Assume that for a set of 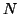 subjects we model their hæmodynamic
response functions using the same set of
subjects we model their hæmodynamic
response functions using the same set of 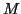 basis functions for each
subject and consider the case where we wish to test for the population
mean activation. Thus, we implicitly assume that there exists a single
hæmodynamic response function that is representative for the group
activation. We will not restrict the choice of basis functions
(i.e. we do not require the basis functions to be orthogonal) and
therefore allow for general correlations between the individual basis
funtion fits, but assume that the covariance structure is the same for
each individual. That is, we model the subject-specific vector of
fits as distributed according to a multivariate normal distribution
and let
where
basis functions for each
subject and consider the case where we wish to test for the population
mean activation. Thus, we implicitly assume that there exists a single
hæmodynamic response function that is representative for the group
activation. We will not restrict the choice of basis functions
(i.e. we do not require the basis functions to be orthogonal) and
therefore allow for general correlations between the individual basis
funtion fits, but assume that the covariance structure is the same for
each individual. That is, we model the subject-specific vector of
fits as distributed according to a multivariate normal distribution
and let
where 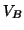 is the covariance matrix of the
is the covariance matrix of the 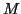 basis function fits. Then the group-level design matrix
combines the
basis function fits. Then the group-level design matrix
combines the 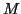 individual basis functions across subjects such that
where the individual values are the
individual basis functions across subjects such that
where the individual values are the 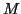 mean basis coefficients. In
order to assess the average population activation, we need to test if
any of the basis function coefficients are significantly non-zero.
This can be achieved by calculating
which approximately follows an
mean basis coefficients. In
order to assess the average population activation, we need to test if
any of the basis function coefficients are significantly non-zero.
This can be achieved by calculating
which approximately follows an 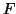 -distribution. If, instead, we wish
to assess if the final
-distribution. If, instead, we wish
to assess if the final 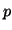 basis functions contribute significantly to
the mean fit, we simply set
and change
basis functions contribute significantly to
the mean fit, we simply set
and change 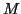 to
to 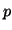 .
.


Next: Conclusion
Up: Examples
Previous: Numerical simulation
Christian Beckmann
2003-07-16
![$\displaystyle V_{\mbox{\tiny\textit{\sffamily {$\!$G}}}}^{\mbox{}}=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}
V_B& & 0 \\
&\ddots & \\
0 & & V_B
\end{array} \right],
$](img204.png)