

Next: Cost Function
Up: Materials
Previous: Materials
The registration problem studied here is to find the best geometric alignment
of two (volumetric brain) images. Call the two images the reference
(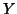 ) and floating (
) and floating (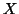 ) images. More precisely, the registration
problem seeks that transformation which, when applied to the floating
image, maximises the ``similarity'' between this transformed floating
image and the reference image.
A standard, and common, way of formulating this as a mathematical
problem is to construct a cost function which quantifies the
dissimilarity between two images, and then search for the
transformation (
) images. More precisely, the registration
problem seeks that transformation which, when applied to the floating
image, maximises the ``similarity'' between this transformed floating
image and the reference image.
A standard, and common, way of formulating this as a mathematical
problem is to construct a cost function which quantifies the
dissimilarity between two images, and then search for the
transformation (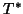 ) which gives the minimum cost. In
mathematical notation this is:
) which gives the minimum cost. In
mathematical notation this is:
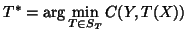 |
(1) |
where 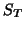 is the space of allowable transformations,
is the space of allowable transformations,
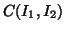 is
the cost function and
is
the cost function and 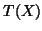 represents the image
represents the image 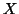 after
it has been transformed by the transformation
after
it has been transformed by the transformation 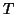 .
In this paper we shall only consider linear registration so that
.
In this paper we shall only consider linear registration so that
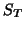 is either the set of all affine transformations or some subset of
this (such as the set of all rigid-body transformations).
is either the set of all affine transformations or some subset of
this (such as the set of all rigid-body transformations).
Peter Bannister
2002-05-03