- ... ICA1
- i.e. by feeding the results of the decomposition into the model-based higher-level analysis
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... subjects2
- restricting
ourselves to a simple single mean-group analysis for the moment.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... (PARAFAC3
- Also known as
'canonical
decomposition' (CANDECOMP [Carroll and Chang, 1970])
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... subjects4
- Note that, similar to the two-dimensional case,
we can freely pass scalar factors between estimates and also
introduce permutations. Absolute amplitude in any of the
factors is only meaningful when fixing all other factors to e.g. unit
standard deviation or unit range.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
convergence5
- e.g. when
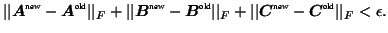
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
model6
- In its general form the multi-level GLM allows to
combine contrasts of lower-level parameter
estimates. Such designs, however, can be re-formulated as
higher-level GLMs operating on simple parameter estimates; see [Beckmann et al., 2003a] for details.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
approximation)7
- In the subject domain, the correlations with
all other processes is not shown, as there are only 3 subjects in this
study
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... map8
- Identified as the map with
highest spatial correlation with the GLM map out of 19 estimated sources; see figure 11
![[*]](icons/crossref.png) (i). Also, the associated time course has highest
correlation with the GLM regressor.
(i). Also, the associated time course has highest
correlation with the GLM regressor.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
normalised9
- Estimated response size between sessions is
normalised to unit standard deviation, thus showing relative response
size only.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... map10
- The model is ambiguous with
respect to scalar factors and signs. The maps presented here have been
scaled manually for comparison.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
solution11
- E.g. approximately 40min for the tensor-PICA estimation
compared to ~8h for PARAFAC on the real FMRI data on a
Compaq Alpha ES40 667MHz Server with Matlab 5.3 (excluding
registration of individual session data to the template space) for the results presented in section 5.2
![[*]](icons/crossref.png) .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.