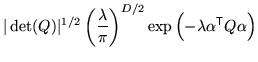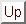

Next: Derivation of Similarity Function
Up: Problem Formulation
Previous: Example
Likelihood is:
Priors:
For 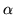 there are two alternative priors that are useful.
there are two alternative priors that are useful.
- Flat prior:
where the range of 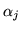 is restricted to
is restricted to
![$ [0,C_1^{-1}]$](img72.png) .
.
- Or a prior encoding prior knowledge:
where 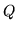 represents the prior knowledge about the expected
intensities in the image formation;
represents the prior knowledge about the expected
intensities in the image formation; 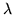 is a parameter
expressing the unknown scaling between the learnt prior distribution
of
is a parameter
expressing the unknown scaling between the learnt prior distribution
of 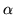 parameters and the intensities in a new image; and
parameters and the intensities in a new image; and 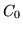 is a constant, representing the (improper) flat prior on
is a constant, representing the (improper) flat prior on 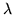 .
.
Parameters:
where
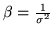 is the precision parameter.
is the precision parameter.


Next: Derivation of Similarity Function
Up: Problem Formulation
Previous: Example
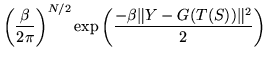
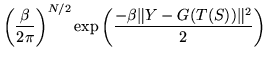
![]() there are two alternative priors that are useful.
there are two alternative priors that are useful.